Diagnosis and Management of Parapneumonic Effusions and.
How a pleural effusion presents depends on several factors such as the size of the effusion, the rate of fluid accumulation, comorbidities, and underlying respira-tory reserve. Patients routinely mention at least one of dyspnoea, cough (non-productive), or chest pain (usu - ally pleuritic). The initial history should be focused on determining the severity and rate of onset of symptoms and thus.
A parapneumonic effusion is any pleural effusion secondary to a bacterial infection of the lung, while a complicated parapneumonic effusion is a parapneumonic effusion that requires tube thoracostomy for its resolution. An empyema is pus in the pleural space; pus by definition is thick, purulent appearing fluid. Most empyemas arise from pneumonias, although about one third of patients with.
Definitions Parapneumonic Effusion Definitions. Parapneumonic Pleural Effusion: effusion which occurs in association with bacterial pneumonia, lung abscess, or bronchiectasis (although an infected pleural effusion may rarely develop without an adjacent pneumonia). Uncomplicated Parapneumonic Effusion: occurs with movement of lung interstitial fluid and neutrophils across the visceral pleural.
Pleural effusion occurs in up to 25% of HIV inpatients and is usually attributable to parapneumonic effusion, TB, Kaposi’s sarcoma, or less commonly lymphoma. 37 Bacterial pneumonia, the commonest cause, carries a 10% inhospital mortality. 38. Benign asbestos pleural effusion. Benign asbestos pleural effusions occur within 20 years after exposure. 39 Typically, there is a small, asymptomatic.
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Prince Tano Djan, BSc, MBChB; Nate Michalak, B.A. Overview. Pleural effusion may be classified according to composition of pleural fluid by Light's criteria into two subtypes: exudate and transudate.An increase in plasma osmotic pressure or elevated systemic or pulmonary hydrostatic pressure are alterations that lead.
Other posts on the site.
Pneumonia is an important health problem in children, and parapneumonic pleural effusion (PPE) is a frequent complication. There is no standard strategy for treating PPE, reflected in the few international guidelines that have been published on the issue. Compared to adults, there is no consensus on the utility of pleural fluid analysis in paediatric PPE. This is because of the lack of good.
Definitions and classification of parapneumonic effusions. A parapneumonic effusion (PPE) refers to any effusion secondary to pneumonia, lung abscess or bronchiectasis. PPEs are divided into three groups: uncomplicated (UPPE), complicated (CPPE) and empyema 11. An UPPE resolves with antibiotic therapy alone, without pleural space sequelae. A.
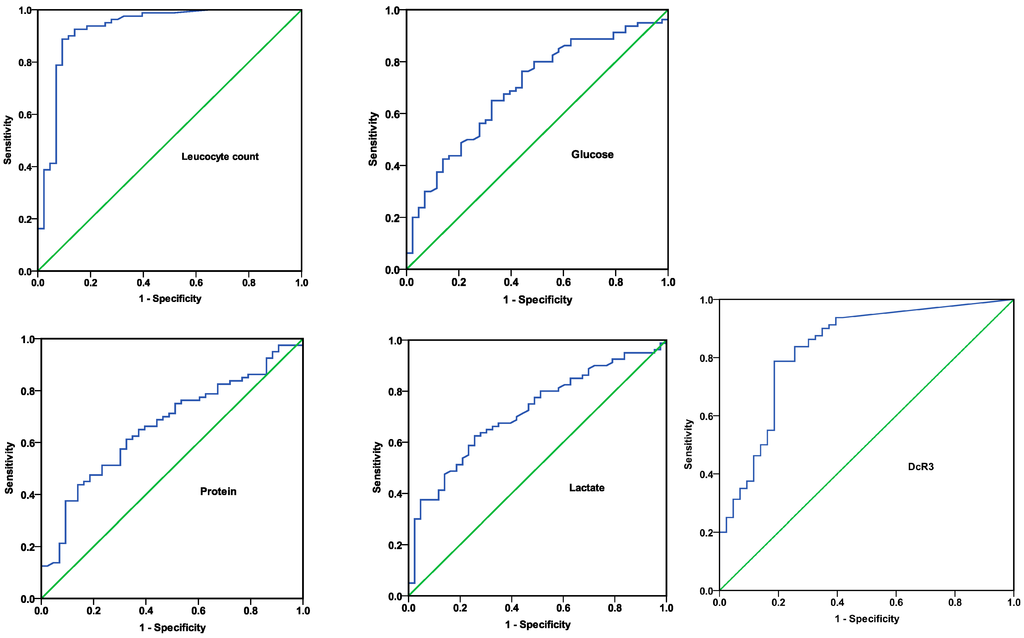
The best indication of the transition from an uncomplicated parapneumonic effusion to a complicated parapneumonic effusion is: (1) Enlarging pleural fluid meniscus on chest radiograph: 2 (2) Altered pleural fluid contour on chest radiograph: 4 (3) Chest pain and persistent fever: 19 (4) Pleural fluid pH, glucose, and lactate dehydrogenase: 39.
Parapneumonic Pleural Effusion Parapneumonic pleural effusion (PPPE) is associated with pulmonary infection, usually pneumonia, abscess, or infected bronchiectasis. Between 20% and 57% of bacterial pneumonias are accompanied by PPPE during their clinical course and approximately 40% of these are complicated PPPE or empyema. 9 Therefore, PPE should be considered in all patients with pneumonia.
Parapneumonic effusions and empyema are more common in boys, in infants and young children, and in winter and spring, presumably because of their infective origin. Streptococcus pneumoniae is currently the most common pathogen in the UK, but a number of other pathogens can also be implicated. Empyema is a significant cause of morbidity, but fortunately not mortality, in children, and at times.
The leading underlying diagnoses associated with pleural effusions are CHF, pneumonia, malignancy, pulmonary embolus, viral disease, coronary artery bypass surgery, and cirrhosis with ascites. 3 The clinical examination is used not so much to determine whether the patient has a pleural effusion but to identify patients that require diagnostic imaging to rule out a pleural effusion.
A pleural effusion is excess fluid that accumulates in the pleural cavity, the fluid-filled space that surrounds the lungs.This excess fluid can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs. Various kinds of pleural effusion, depending on the nature of the fluid and what caused its entry into the pleural space, are hydrothorax (serous fluid), hemothorax (blood), urinothorax (urine.
Parapneumonic pleural effusion: reality and strategies in an Amazon University Hospital 425 Rev. Col. Bras. Cir. 2016; 43(6): 424-429 conversion into open thoracic drainage (OTD) for the refractories. It also found that classic thoracotomy was hardly performed, and yet the discharge of patients in good general condition was the rule.